Gas Instant Water Heater: The Smart Choice for Instant Hot Water
In modern homes, convenience and efficiency go hand in hand and when it comes to hot water, nobody wants to wait. That’s where a Gas Instant Water Heater comes in. This device heats water on demand using gas, delivering hot water almost instantly rather than storing heated water in a large tank. As more households seek quick, energy-efficient solutions, gas instant water heaters are gaining popularity for their compactness, low standby losses, and ability to respond immediately to your hot water needs. Below, we explore the benefits, working principles, installation considerations, maintenance needs, safety precautions, and buying tips to help you decide whether a gas instant water heater is right for your home.
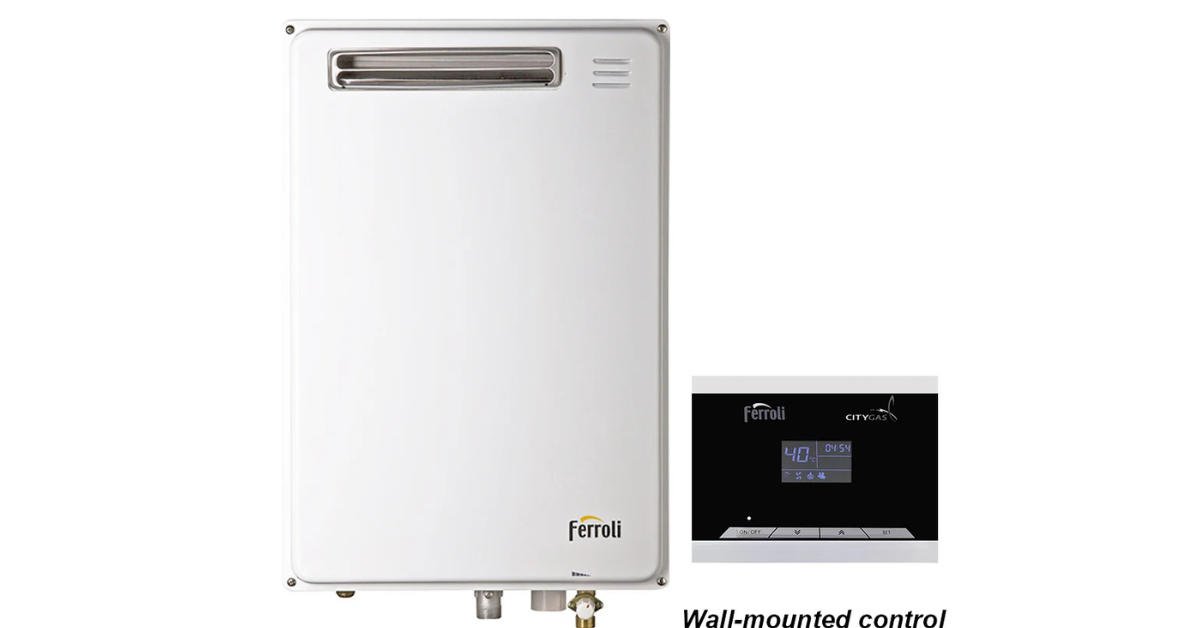
What Is a Gas Instant Water Heater?
A gas instant water heater (also called a tankless or on-demand heater) heats water directly as it flows through the unit. When a user turns on a hot water tap, cold water enters the heater, passes through a heat exchanger, and is heated by gas combustion. The result: hot water at the tap almost immediately no waiting, no storage tank. Because it only heats water in real time, there is no standby heat loss that you get with traditional storage water heaters.
Advantages of Using a Gas Instant Water Heater
1. Instant Hot Water on Demand
One of the most compelling benefits is that you don’t have to wait for water to warm up. The heater only activates when you open the tap, making it ideal for households where multiple people may need hot water in quick succession.
2. Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Since the heater only runs when hot water is needed, there’s no wasted energy keeping a tank of water hot 24/7. Over time, this can lead to savings on utility bills, especially in settings where gas is cheaper than electricity.
3. Compact and Space-Saving Design
Because there’s no bulky storage tank, gas instant water heaters are much smaller and easier to fit into tight spaces such as small bathrooms, utility closets, or under sinks.
4. Unlimited Hot Water (Within Capacity)
As long as the demand stays within the unit’s capacity, you won’t “run out” of hot water, unlike conventional tank heaters which can be depleted and need reheating.
5. Lower Environmental Impact
Reduced energy waste and the absence of continuous heating make tankless systems more environment-friendly, contributing to lower greenhouse gas emissions over time.
6. Longer Lifespan
Because there’s no large tank subject to corrosion, gas instant heaters often last longer than traditional storage water heaters, with fewer parts to fail.
How a Gas Instant Water Heater Works
Here’s a simplified overview of its operation:
-
Cold Water Inlet — When you turn on a hot tap, cold water enters the heater.
-
Flow Sensor / Trigger — A flow sensor detects movement. When it senses it, it signals the gas valve to open and ignition to start.
-
Gas Combustion — Gas is ignited and burners heat the heat exchanger.
-
Heat Exchange — Water passes through the exchanger where it absorbs heat from the combustion gases.
-
Outlet to Tap — The heated water then flows out to your shower, faucet, or other point of use.
-
Controls & Sensors — Temperature sensors and safety devices monitor pressure, flame presence, and prevent overheating or gas leaks.
Because the heating is instantaneous and only active when in use, the system remains energy-efficient. Advanced models may include modulating gas valves, which scale the flame according to flow, further optimizing gas usage.
Considerations Before Installing a Gas Instant Water Heater
1. Gas Supply and Type
You need a reliable gas supply (natural gas or LPG, depending on your region). The gas piping must support the flow and pressure required by the heater, and conform to safety codes.
2. Ventilation and Exhaust
Since combustion is involved, proper venting is critical. The system needs to exhaust combustion gases safely outdoors, and adequate air intake must be provided to avoid carbon monoxide buildup.
3. Water Pressure and Flow Rate
Tankless heaters require a minimum water flow to trigger activation. If your household has low water pressure, certain models may not perform well. Also, your instantaneous demand should match the heater’s capacity (liters per minute, or L/min).
4. Installation Location
Choose a location close to your main demand points while ensuring enough space for venting, servicing, and clearances as per manufacturer specifications.
5. Matching Capacity to Demand
If more than one hot water outlet (e.g. shower + sink) may be in use simultaneously, you’ll need a heater with sufficient capacity to manage the combined flow without reducing temperature dramatically.
6. Safety Measures
You must include gas safety shutoffs, flame sensors, overheat protection, and possibly anti-scalding features. Complying with local building, gas, and safety codes is essential.
Maintenance and Safety Guidelines
Regular Maintenance
-
Annual Inspection — Have a qualified technician inspect burners, heat exchanger, gas lines, and venting.
-
Descaling / Flushing — In areas with hard water, mineral buildup can reduce performance. Periodic flushing with vinegar or descaling agents can preserve efficiency.
-
Filter Cleaning — If the unit has inlet filters or screens, clean them to prevent flow restrictions.
-
Check for Leaks — Regularly inspect gas connections and plumbing joints for corrosion or leaks.
-
Pilot / Ignition System — Ensure the ignition device and sensors remain clean and function properly.
Safety Precautions
-
Install Carbon Monoxide Detectors — As combustion occurs, any gas heater runs a risk of CO leakage if venting is compromised.
-
Proper Venting and Air Supply — Never seal off air intake or block vents.
-
Install Pressure Relief Valves — Use safety valves to prevent dangerous pressure buildup.
-
Avoid DIY Gas Work — Always use licensed professionals for gas piping, venting, and servicing.
-
Temperature Limits — Set a safe maximum temperature (e.g. 50–55 °C) to prevent scalding.
Use Cases and Applications
Gas instant water heaters are ideal in a variety of scenarios:
-
Urban Apartments — Where space is premium and demand is moderate.
-
Single or Double Bathroom Homes — To support showers and minimal simultaneous usage.
-
Commercial Settings — Such as small offices, salons, or laundries where quick, on-demand heating is required.
-
Backup or Secondary Systems — For kitchens or guest bathrooms where hot water is needed intermittently.
However, in very large homes with high simultaneous demand across many bathrooms, multiple units or hybrid systems might be necessary.
Potential Drawbacks and Limitations
While gas instant water heaters offer many benefits, it’s important to be aware of some challenges:
-
Higher Upfront Cost — These units (and their installation) often cost more initially than simple storage water heaters.
-
Minimum Flow Requirements — If you draw very small amounts of water, the heater might not activate.
-
Gas Dependence — If gas supply is interrupted or the system fails, you lose heating instantly.
-
Complex Installation — Venting, gas lines, and safety compliance make installation more involved.
-
Water Temperature Fluctuations — If demand exceeds capacity or flow changes, output temperature may drop unless the unit is oversized.
How to Choose the Right Gas Instant Water Heater
When shopping for a gas instant water heater, consider these important factors:
1. Flow Rate / Capacity
Check the heater’s rated flow (e.g. in L/min) and match it to your peak demand: showers, faucets, etc.
2. Temperature Rise
Determine how many degrees of heating the unit must supply. For example, if cold water comes in at 20 °C and you want 50 °C output, the unit must provide a 30 °C temperature rise at the required flow.
3. Efficiency / Energy Rating
Look for high efficiency ratings or certification marks. More efficient units convert more gas into hot water with less waste.
4. Safety Features
Ensure the model includes safeguards like flame failure sensors, overheat protection, and anti-scald control.
5. Venting Type
Decide whether a direct vent, power vent, or natural draft system suits your building layout.
6. Brand Reputation and Service
Select a reliable brand with good after-sales support and availability of spare parts.
7. Warranty
Check the warranty period both for the unit and heat exchanger since this is an important indicator of durability.
Future Trends and Innovations
Gas instant water heaters are evolving with technology:
-
Smart / Wi-Fi Connectivity — Some units now feature remote temperature controls, usage tracking, and diagnostics through your smartphone.
-
Modulating Burners — Advanced units can vary gas usage depending on the flow demand, achieving better efficiency.
-
Compact Designs — Manufacturers are refining designs to deliver better performance in even smaller footprints.
-
Hybrid Systems — Combining gas instant heaters with solar preheating or heat pumps to reduce gas consumption further.
-
Improved Safety Electronics — With more sensitive sensors and automatic shutoffs, newer units are even safer than before.
Conclusion
In a world that demands convenience, efficiency, and sustainability, gas instant water heaters provide a compelling solution for instant hot water without the energy waste of traditional tank systems. They are well suited for compact homes, moderate hot water usage, and applications where space is limited. While the initial cost and installation complexity may be higher, the long-term energy savings, extended lifespan, and improved user experience often justify the investment.
If you’re considering upgrading to a gas instant water heater, take time to assess your hot water demand, local gas infrastructure, venting options, and safety requirements. With the right choice, you’ll enjoy the luxury of hot water on demand anytime you need it.